CTE, Trades and Apprenticeships
Pre-existing pathways are a great way to start teaching green skills. Programs for electricians, manufacturing and more are a fantastic place to start.
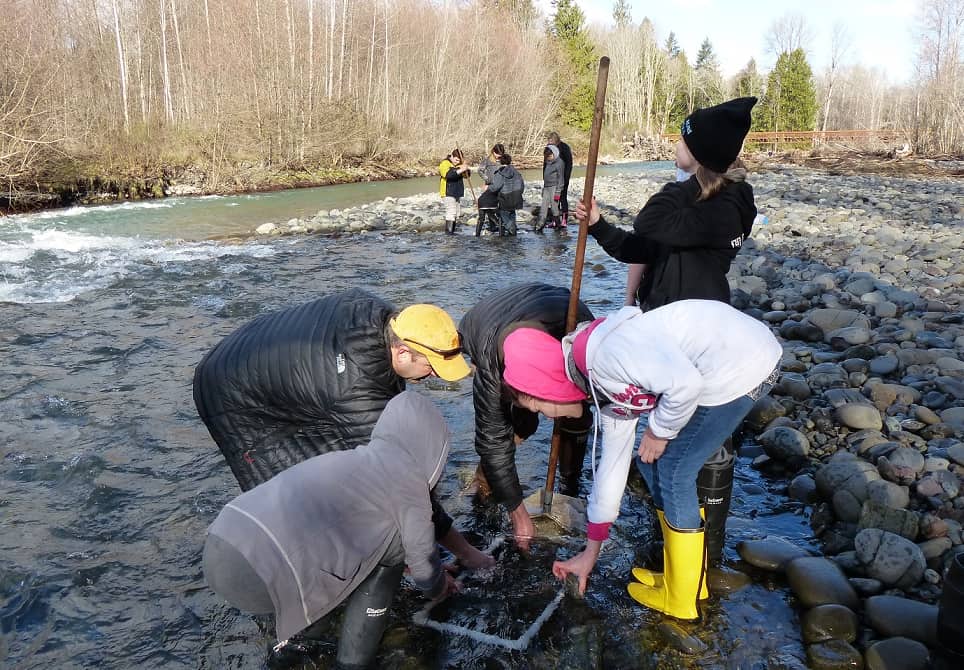

Key Takeaways

CTE's Promise
CTE has the potential to offer early exposure to students regarding green career options by receiving the most relevant training necessary so they are equipped for future workforce demands.

Work-Based Postsecondary Opportunity
Paid work-based learning and certification programs are being offered around the country at the high school, college and postsecondary and postgraduate levels for pathway to career opportunities to combat climate change.

Sustaining Microschools
Microschools centered on sustainability and green pathways can be the models for the rest of a school district to see what is possible and then scaled.
Career Technical Education (CTE) provides pathways for students to build the knowledge and skills necessary to be postsecondary and workforce ready. CTE has the potential to offer early exposure to students regarding green career options by receiving the most relevant training necessary so they are equipped for future workforce demands. Whether new jobs or the reshaping of existing jobs, secondary education, postsecondary education, and industry partners all must work together to ensure that students are prepared for the green jobs of the future.
Unfortunately, stigmas associated with blue-collar careers and a bias towards college-ready pathways have caused a drop in courses that give students hands-on skills. Perhaps exposure to clean energy, through applied, elective courses or CTE could encourage students to gain an interest in this field and visualize a pathway as to how they might do their part professionally to facilitate this transition. (A map of over 40 careers in solar alone)
To prepare for the green economy, a more coordinated effort is needed to align workforce needs with CTE programs; the current system is reactive rather than proactive. In order to meet the needs of local businesses, provide purpose-driven pathway options for students, and satisfy the growing demand for green skills, the workforce ecosystem will require all parts to be interconnected.
Schools are uniquely positioned to facilitate education to employment opportunities based on the needs of their communities. Investments to refurbish old factories into clean manufacturing might provide a different set of opportunities than a community based in the Sun Belt investing in solar; climate change affects different places in different ways and therefore the response needs to be adapted to local needs. Schools have the capacity to engage in or facilitate the sorts of community partnerships that will help students to pave their way in this new economy.
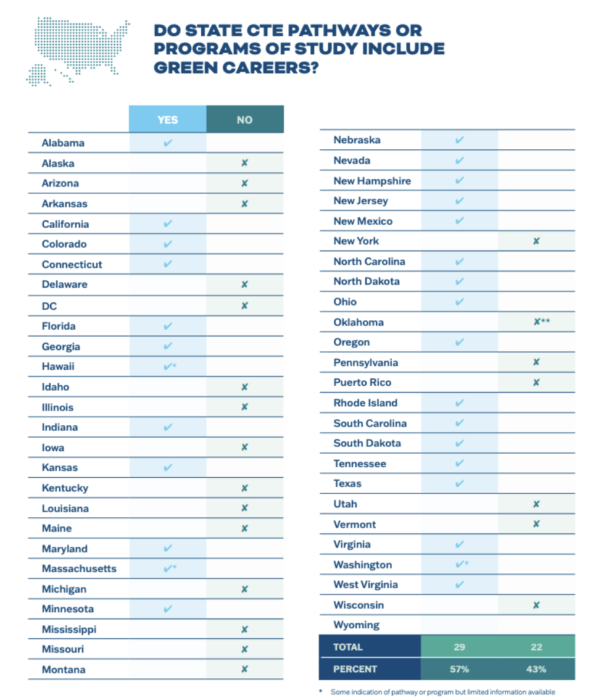
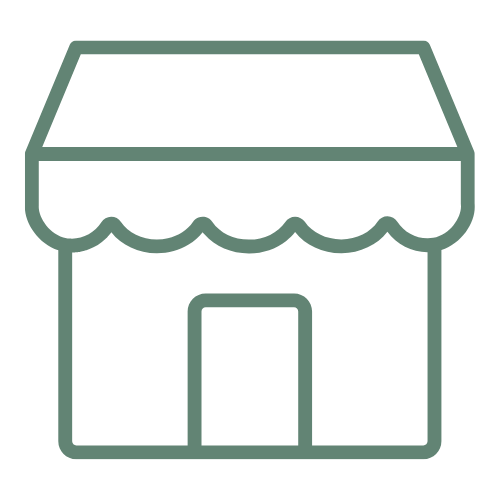
This is Planet ED
A few years ago This is Planet ED, an initiative the Aspen Institute identified the progress of green embedded CTE programs by state.
Work-Based Learning
Work-based learning opportunities can support college and career readiness by providing on-the-job training while students are still in high school. Employers are increasingly recognizing the value of work-based learning in addressing the skills gap, and some industries, such as the energy industry, are implementing apprenticeships and internships to develop a workforce pipeline to specific careers or postsecondary programs so that students are ready before they even graduate high school to address the quickly growing need for green career skills.
Apprenticeships
In many apprenticeship programs, students can gain work experience, build a social network, and earn an industry certification, college credit and a paycheck. Apprenticeships ensure an industry-driven approach to green career pathway opportunities, which benefits both the employer and student by preparing students for careers that are grounded in the current needs of the local workforce. Paid work-based learning and certification programs are being offered around the country at the high school, college and postsecondary and postgraduate levels for a pathway to career opportunities to combat climate change. Schools and communities need to be making these connections for the benefit of their learners.

ReVision Energy Electrical Apprenticeship Program (REEAP)
Offered in Maine, Massachusetts, and New Hampshire, REAP is geared towards those interested in growing the solar workforce, who have graduated high school with a diploma or GED, or for those with a college degree, to provide a solution to the labor shortage in the industry. Providing a pathway to a career as a Solar Installer or Solar Service Technician, ReVision offers a four-year program of instruction alongside renewable energy electricians with a complementary schedule of on-the-job, online and in-person training. On top of it all, the cost of the apprenticeship program is covered by the Training Center.

Florida Solar Pathways
Florida is building out a solar energy apprenticeship program as a pathway to state certification in both solar electric and thermal systems. Established by way of a partnership between the Florida Solar Energy Industries Association (FlaSEIA) and the Florida Solar Energy Center (FSEC), it is the first such apprenticeship program in the U.S. to be registered with the Department of Labor. The two-year apprenticeship program is currently recruiting industry employers and interested participants.

Green Jobs Corps
Common Ground is a high school, urban farm, and environmental education center in Connecticut. Green Jobs Corps is a paid internship program offered through Common Ground, in partnership with Yale’s Urban Resource Initiative and other local organizations such as CitySeed, Save the Sound, and the Regional Water Authority. High school students take on tending the urban farm, creating green spaces, developing school gardens, planting trees and running farmer’s markets across the city of New Haven. Students earn a stipend while gaining valuable environmental career experience through opportunities that directly serve their community.

Climate Fellowships
“ClimateFellowships.com makes it easy to locate environmental, sustainability, climate, and green fellowships. These opportunities can serve as a vital pathway to enable students and recent graduates to obtain their first job in this sector.
The initial focus of this site is to highlight fellowships that provide the recipient with paid, summer or full-time employment or funding for action (such as scientific research, launching a startup, etc.).”

Connecticut Technical Education and Career System (CTECS)
CTECS is a state-run vocational education program that offers high-quality technical education to students in Connecticut. Whether looking to enter the workforce immediately or continue their education at a higher level, CTECS offers over 30 CTE programs, early college in high school credit, and a robust work-based learning program. Five of these CTE programs include green pathways or embed green skills in the program; for example, the Architecture pathway includes curriculum on sustainable building technologies and students enrolled in the HVAC program will also obtain instruction in energy efficiency, environmental, renewable energy, as well as energy conservation practices.

Climate Scholars
The City University of New York (CUNY) offers a Climate Scholars fellowship to students at their four branches, in which college students can earn a stipend while researching and exploring future careers in green energy. Students across all majors are welcome to participate in the six month fellowship. The first half of the fellowship is geared towards research and the second half is an internship which involves teaching local high school and middle school students about climate change and renewable energy innovations.
Credentialing Examples
Credentialed learning provides a more clearly defined connection between K12, college and career, making learning more relevant and aligned to what students need to know and be able to do, whether entering postsecondary education and/or the workforce. Too often, CTE courses geared toward sustainability are offered as one-off or elective-style courses. School districts need to offer green CTE pathway programs that lead toward an industry-recognized credential (IRC) or college credit in high school in order to prepare students for the pressing need for green jobs. Credentials, micro-credentials and badges are all ways that students can show they have skills that align with postsecondary and/or industry needs and can be another way to address the skills gap in the green sector.
Tacoma Public Schools
Tacoma Public Schools offers nine summer credential programs, one of which is the Environmental Services Program. In this 90-hour program, students can earn a small stipend, 0.5 credit towards high school graduation and multiple certifications, including completion of the Certified Erosion & Soil Control Lead which prepares students to protect natural habitats from soil erosion. This program is a gateway to multiple career pathways in environmental sciences.

Olathe Public Schools
Olathe Public Schools embeds 21st Century Academies within all four of their comprehensive high schools. Olathe West High School houses the Green Tech Academy which provides pathways to green careers in sustainable agriculture and renewable energy. Students engage in real world learning through field trips and multiple project-based and community experiences. Through the completion of a CTE pathway at the Green Tech Academy students earn a 21st Century Academy endorsement designated on their transcript, plus the opportunity to earn an industry-recognized credential.
Additional Credentials
The following additional credentials have been mentioned in conversations with numerous pioneers in this sector, as well as on the following lists: Better Buildings Solutions Center and the National Center for Construction Education and Research NCCER:
- CPR
- Certification in energy auditing (BPI, HEP, RESNET HERS)
- EIF
- NIMS
- LEED Green
- WorkKeys NCRC
- CDL
- Refrigeration License
- FAA Drone Operator
- CAST
- CESCL (Certified Erosion & Soil Control Lead)
- GPRO – Fundamentals of Building Green
P-TECH Examples
In 2011 IBM infused work experiences and employment opportunities into the dual enrollment model and supported the development of Pathways in Technology Early College High School (P-TECH). These schools focus on durable skills such as good work habits and interpersonal skills, as well as technical skills that are specific to the program and community partnerships. P-TECH requires coordination between secondary, postsecondary, and employers which lays the foundation for opportunities to integrate green skills and lead to green jobs. Utilities companies have a huge opportunity for playing more of a role in this transition as well. Find out more about P-TECH on their Getting Started page.

TEC-SMART
The Training and Education Center for Semiconductor Manufacturing and Alternative and Renewable Technologies (TEC-SMART), a part of the Hudson Valley Community College system, trains students to enter the workforce through the lens of environmental sustainability and technological innovation. TEC-SMART also houses the Clean Technologies and Sustainabilities Early College High School (ECHS), a P-TECH which offers students four pathways in clean energy. With support from local organizations, the ECHS collaborates with hundreds of businesses, higher ed, K12, and industry with the shared vision to develop a workforce pipeline to jobs in the green economy.

Eagle County School District
Eagle County School District hosts P-TECH programs at two of their high schools offering students a pathway in Environmental Solutions. In partnership with Colorado Mountain College and local organizations, students can graduate high school with an Associate’s in Environmental Studies that can bridge to a Bachelor’s in Environmental Studies or students can take advantage of Colorado Mountain College’s certification program in Environmental Leadership.
Dual Enrollment Examples
Dual enrollment offers students the opportunity to concurrently earn high school and college credit, to get a jumpstart on college classes and to explore a career pathway; oftentimes the school district will cover the cost of the college credit which expands access and opportunity especially for students from historically marginalized backgrounds. This can accelerate a student’s completion of a degree or certification, in many cases without a significant burden of debt, allowing them to kickstart a career sooner, especially in the growing and demanding field of green jobs.

Wonderful Agriculture Career Prep
In California’s Central Valley, Wonderful Agriculture Career Prep makes the most of the large agricultural industry in the area and offers a program where students can earn an Associate of Science degree while in high school, tuition free, including 60 college credits and over 200 hours of paid internship experience. Students can either enter the workforce into a guaranteed job or head on to a four year university (in which half of the cost has already been paid for and half of the credits have already been completed).

New York Harbor School
New York Harbor School offers seven CTE career pathways, leading to industry certification in marine science or technology and also includes a continuum of work-based learning experiences. Each of the seven CTE programs are geared towards environmental restoration and students take the lead on local ecosystem restoration through real world learning experiences. During freshman year, students are introduced to all seven pathways and as a sophomore they pick which one they would like to focus on. The Billion Oyster Project, a plan to restore one billion live oysters to the local marine ecosystem, is a partnership between the Harbor School and community partnerships from the local level all the way up to the federal level; embedded in the CTE programs, it is considered a world-wide model of engaging youth in ecosystem restoration practices.

Oakland Skyline Pathways
Students in the Oakland Skyline Pathways explore careers in the energy sciences such as solar and wind design and installation, green chemistry, green architecture, interior building design, green construction, electrical systems, waste management, research science, environmental science, public transportation and more. Two key partnerships are Laney College’s Green Technology program and Merritt College’s Urban Agroecology program. Students are encouraged to participate in these college programs while still in high school and to take advantage of mentorship offerings that will support them in future goals in any environment-related field.
Green Microschools Examples
Microschools are small schools that are typically embedded within a larger school, often with a focus area such as career exploration or sustainability. Their size allows them to be established in alternative spaces and leverage community assets while making learning more personal. Microschools centered on sustainability and green pathways can be the models for the rest of a school district to see what is possible and then scaled.

School of Environmental Leadership
The School of Environmental Leadership (MarinSEL), a program of SEI, is a microschool located within Terra Linda High School in Marin County. Strong academics are enhanced through project-based learning, creative arts and service to the community, all through the lens of environmental stewardship. It’s a four-year program with green embedded throughout, culminating senior year with a year-long internship focused on the environment.

The Green Academy
The Green Academy at Abraham Lincoln High School in the Bay Area teaches students to create new solutions to environmental challenges. The capstone project during senior year is to develop a community service project. In partnership with Generation Citizen, students are empowered to identify a need in their community and petition the policymakers to make a change.

Environmental Science Academy
A microschool nestled within Oakland High School, the Environmental Science Academy provides a three-year course sequence for students focused on community activism and problem-solving in relation to climate and sustainability, including work-based learning experiences and even a student-operated field station. The pathway program has been around for over 20 years and remains relevant with the increasing impact of climate change.

WELS at Tyee High School
WELS at Tyee High School is a CTE pathway that develops a stewardship mindset in students and offers career exploration in environmental and education fields. Students take two years of coursework in which they receive work-based learning experiences in partnership with local green industries. Students spend sophomore and junior year gaining outdoor leadership skills, partnering with various environmental agencies and exploring green jobs.

REAL Academy
Students at the REAL Academy within Desert Hot Springs High School learn about clean and renewable energy. With business partners like Hot Purple Energy, a local solar company in Palm Springs, students gain green skills and prepare for careers in green energy. They follow the Linked Learning model to ensure students are prepared for college and career by graduation.

Koshkonong Trails School
Koshkonong Trails School, a charter microschool within the School District of Cambridge, is on a mission to “provide a place-based, experiential education built around conservation, stewardship, and agriculture.” A project-based middle and high school situated on a 20-acre farmstead, the school utilizes place-based learning to explore trails, a wetland, quarry, pond and a community garden.

Environmental Charter High School
Environmental Charter High School in Los Angeles was the first recipient of the US Department of Education Green Ribbon, a distinction that shows a school community is committed to renewable energy practices and embedding sustainability education into curriculum. Through outdoor education, the Green Ambassadors program, holding a community-wide Earth Carnival, and an advocacy trip to Washington D.C. by way of the Pacific Crest Trail, to list a few, students are prepared to become environmental leaders in their communities.